BIP 0070: Difference between revisions
Payment Protocol |
m Fix formatting |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
The current, minimal Bitcoin payment protocol operates as follows: | The current, minimal Bitcoin payment protocol operates as follows: | ||
# Customer adds items to an online shopping basket, and decides to pay | # Customer adds items to an online shopping basket, and decides to pay using Bitcoin. | ||
using Bitcoin. | # Merchant generates a unique payment address, associates it with the customer's order, and asks the customer to pay. | ||
# Merchant generates a unique payment address, associates it with the | # Customer copies the Bitcoin address from the merchant's web page and pastes it into whatever wallet they are using OR follows a bitcoin: link and their wallet is launched with the amount to be paid. | ||
customer's order, and asks the customer to pay. | # Customer authorizes payment to the merchant's address and broadcasts the transaction through the Bitcoin p2p network. | ||
# Customer copies the Bitcoin address from the merchant's web page and pastes | # Merchant's server detects payment and after sufficient transaction confirmations considers the transaction final. | ||
it into whatever wallet they are using OR follows a bitcoin: link and | |||
their wallet is launched with the amount to be paid. | |||
# Customer authorizes payment to the merchant's address and broadcasts the | |||
transaction through the Bitcoin p2p network. | |||
# Merchant's server detects payment and after sufficient transaction | |||
confirmations considers the transaction final. | |||
This BIP extends the above protocol to support several new features: | This BIP extends the above protocol to support several new features: | ||
# Human-readable, secure payment destinations-- customers will be asked to | # Human-readable, secure payment destinations-- customers will be asked to authorize payment to "website.com" instead of an inscrutable, 34-character | ||
authorize payment to "website.com" instead of an inscrutable, 34-character | |||
bitcoin address. | bitcoin address. | ||
# Secure proof of payment, which the customer can use in case of a | # Secure proof of payment, which the customer can use in case of a dispute with the merchant. | ||
dispute with the merchant. | # Payment received messages, so the customer knows immediately that the merchant has received, and has processed (or is processing) their payment. | ||
# Payment received messages, so the customer knows immediately that the | # Refund addresses, automatically given to the merchant by the customer's wallet software, so merchants do not have to contact customers before refunding | ||
merchant has received, and has processed (or is processing) their payment. | |||
# Refund addresses, automatically given to the merchant by the customer's wallet | |||
software, so merchants do not have to contact customers before refunding | |||
overpayments or orders that cannot be fulfilled for some reason. | overpayments or orders that cannot be fulfilled for some reason. | ||
| Line 165: | Line 155: | ||
authorize payment by doing the following: | authorize payment by doing the following: | ||
# Validate the merchant's identity and signature using the PKI | # Validate the merchant's identity and signature using the PKI system, if the pki_type is not "none". | ||
system, if the pki_type is not "none". | # Validate that the time on the customer's system is before PaymentDetails.expires. If it is not, then the payment request | ||
# Validate that the time on the customer's system is before | |||
PaymentDetails.expires. If it is not, then the payment request | |||
must be rejected. | must be rejected. | ||
# Display the merchant's identity and ask the customer if they would | # Display the merchant's identity and ask the customer if they would like to submit payment (e.g. display the "Common Name" in the first X.509 certificate). | ||
like to submit payment (e.g. display the "Common Name" in the first | |||
X.509 certificate). | |||
PaymentRequest messages larger than 50,000 bytes should be rejected by | PaymentRequest messages larger than 50,000 bytes should be rejected by | ||
| Line 204: | Line 190: | ||
If the customer authorizes payment, then the Bitcoin client: | If the customer authorizes payment, then the Bitcoin client: | ||
# Creates and signs one or more transactions that satisfy (pay in | # Creates and signs one or more transactions that satisfy (pay in full) PaymentDetails.outputs | ||
full) PaymentDetails.outputs | |||
# Broadcast the transactions on the Bitcoin p2p network. | # Broadcast the transactions on the Bitcoin p2p network. | ||
# If PaymentDetails.payment_url is specified, POST a Payment message | # If PaymentDetails.payment_url is specified, POST a Payment message to that URL. The Payment message is serialized and sent as the body of the POST request. | ||
to that URL. The Payment message is serialized and sent as the body | |||
of the POST request. | |||
Errors communicating with the payment_url server should be communicated to the user. | Errors communicating with the payment_url server should be communicated to the user. | ||
Revision as of 01:55, 31 July 2013
|
This page describes a BIP (Bitcoin Improvement Proposal). |
BIP: 70 Title: Payment Protocol Author: Gavin Andresen <gavinandresen@gmail.com> Status: Draft Type: Standards Track Created: 29-07-2013
Abstract
This BIP describes a protocol for communication between a merchant and their customer, enabling both a better customer experience and better security against man-in-the-middle attacks on the payment process.
Motivation
The current, minimal Bitcoin payment protocol operates as follows:
- Customer adds items to an online shopping basket, and decides to pay using Bitcoin.
- Merchant generates a unique payment address, associates it with the customer's order, and asks the customer to pay.
- Customer copies the Bitcoin address from the merchant's web page and pastes it into whatever wallet they are using OR follows a bitcoin: link and their wallet is launched with the amount to be paid.
- Customer authorizes payment to the merchant's address and broadcasts the transaction through the Bitcoin p2p network.
- Merchant's server detects payment and after sufficient transaction confirmations considers the transaction final.
This BIP extends the above protocol to support several new features:
- Human-readable, secure payment destinations-- customers will be asked to authorize payment to "website.com" instead of an inscrutable, 34-character
bitcoin address.
- Secure proof of payment, which the customer can use in case of a dispute with the merchant.
- Payment received messages, so the customer knows immediately that the merchant has received, and has processed (or is processing) their payment.
- Refund addresses, automatically given to the merchant by the customer's wallet software, so merchants do not have to contact customers before refunding
overpayments or orders that cannot be fulfilled for some reason.
Protocol
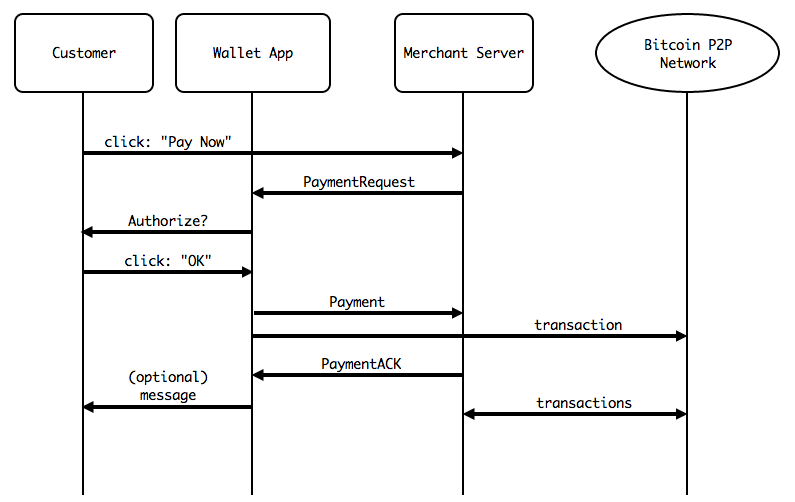
This BIP describes payment protocol messages encoded using Google's Protocol Buffers, authenticated using X.509 certificates, and communicated over http/https. Future BIPs might extend this payment protocol to other encodings, PKI systems, or transport protocols.
The payment protocol consists of three messages; PaymentRequest, Payment, and PaymentACK, and begins with the customer somehow indicating that they are ready to pay and the merchant's server responding with a PaymentRequest message:
Messages
Output
Outputs are used in PaymentRequest messages to specify where a payment (or part of a payment) should be sent. They are also used in Payment messages to specify where refund should be sent.
message Output {
optional uint64 amount = 1 [default = 0];
optional bytes script = 2;
}
| amount | Number of satoshis (0.00000001 BTC) to be paid |
| script | a "TxOut" script where payment should be sent. This will normally
be one of the standard Bitcoin transaction scripts (e.g. pubkey OP_CHECKSIG). This is optional to enable future extensions to this protocol that derive Outputs from a master public key and the PaymentRequest data itself. |
PaymentDetails/PaymentRequest
Payment requests are split into two messages to support future extensibility. The bulk of the information is contained in the PaymentDetails message. It is wrapped inside a PaymentRequest message, which contains meta-information about the merchant and a digital signature.
message PaymentDetails {
optional string network = 1 [default = "main"];
repeated Output outputs = 2;
required uint64 time = 3;
optional uint64 expires = 4;
optional string memo = 5;
optional string payment_url = 6;
optional bytes merchant_data = 7;
}
| network | either "main" for payments on the production Bitcoin
network, or "test" for payments on test network. If a client receives a PaymentRequest for a network it does not support it must reject the request. |
| outputs | one or more outputs where Bitcoins are to be sent. If the
sum of outputs.amount is zero, the customer will be asked how much to pay, and the bitcoin client may choose any or all of the Outputs (if there are more than one) for payment. If the sum of outputs.amount is non-zero, then the customer will be asked to pay the sum, and the payment shall be split among the Outputs with non-zero amounts (if there are more than one; Outputs with zero amounts shall be ignored). |
| time | Unix timestamp (seconds since 1-Jan-1970) when the
PaymentRequest was created. |
| expires | Unix timestamp after which the PaymentRequest should be
considered invalid. |
| memo | UTF-8 encoded, plain-text (no formatting) note that should be
displayed to the customer, explaining what this PaymentRequest is for. |
| payment_url | Secure (usually https) location where a Payment
message (see below) may be sent to obtain a PaymentACK. |
| merchant_data | Arbitrary data that may be used by the merchant to
identify the PaymentRequest. May be omitted if the merchant does not need to associate Payments with PaymentRequest or if they associate each PaymentRequest with a separate payment address. |
A PaymentRequest is PaymentDetails optionally tied to a merchant's identity:
message PaymentRequest {
optional uint32 payment_details_version = 1 [default = 1];
optional string pki_type = 2 [default = "none"];
optional bytes pki_data = 3;
required bytes serialized_payment_details = 4;
optional bytes signature = 5;
}
| payment_details_version | See below for a discussion of versioning/upgrading. |
| pki_type | public-key infrastructure (PKI) system being used to
identify the merchant. All implementation should support "none", "x509+sha256" and "x509+sha1". |
| pki_data | PKI-system data that identifies the merchant and can be
used to create a digital signature. In the case of X.509 certificates, pki_data one or more X.509 certificates (see Certificates section below). |
| serialized_payment_details | A protocol-buffer serialized
PaymentDetails message. |
| signature | digital signature over a hash of the protocol buffer
serialized variation of the PaymentRequest message, where signature is a zero-byte array and fields are serialized in numerical order (all current protocol buffer implementations serialize fields in numerical order), using the public key in pki_data. |
When a Bitcoin wallet application receives a PaymentRequest, it must authorize payment by doing the following:
- Validate the merchant's identity and signature using the PKI system, if the pki_type is not "none".
- Validate that the time on the customer's system is before PaymentDetails.expires. If it is not, then the payment request
must be rejected.
- Display the merchant's identity and ask the customer if they would like to submit payment (e.g. display the "Common Name" in the first X.509 certificate).
PaymentRequest messages larger than 50,000 bytes should be rejected by the merchant's server, to mitigate denial-of-service attacks.
Payment
Payment messages are sent after the customer has authorized payment:
message Payment {
optional bytes merchant_data = 1;
repeated bytes transactions = 2;
repeated Output refund_to = 3;
optional string memo = 4;
}
| merchant_data | copied from PaymentDetails.merchant_data. Merchants
may use invoice numbers or any other data they require to match Payments to PaymentRequests. |
| transactions | One or more valid, signed Bitcoin transactions that
fully pay the PaymentRequest |
| refund_to | One or more outputs where the merchant may return
funds, if necessary. |
| memo | UTF-8 encoded, plain-text note from the customer to the
merchant. |
If the customer authorizes payment, then the Bitcoin client:
- Creates and signs one or more transactions that satisfy (pay in full) PaymentDetails.outputs
- Broadcast the transactions on the Bitcoin p2p network.
- If PaymentDetails.payment_url is specified, POST a Payment message to that URL. The Payment message is serialized and sent as the body of the POST request.
Errors communicating with the payment_url server should be communicated to the user.
PaymentDetails.payment_url must be secure against man-in-the-middle attacks that might alter Payment.refund_to (if using HTTP, it must be TLS-protected).
When the merchant's server receives the Payment message, it must determine whether or not the transactions satisfy conditions of payment. If and only if they do, if should broadcast the transaction(s) on the Bitcoin p2p network.
PaymentACK
PaymentACK is the final message in the payment protocol; it is sent from the merchant's server to the bitcoin wallet in response to a Payment message:
message PaymentACK {
required Payment payment = 1;
optional string memo = 2;
}
| memo | UTF-8 encoded note that should be displayed to the customer
giving the status of the transaction (e.g. "Payment of 1 BTC for eleven tribbles accepted for processing.") |
Localization
Merchants that support multiple languages should generate language-specific PaymentRequests, and either associate the language with the request or embed a language tag in the request's merchant_data. They should also generate a language-specific PaymentACK based on the original request.
For example: A greek-speaking customer browsing the Greek version of a merchant's website clicks on a "Αγορά τώρα" link, which generates a PaymentRequest with merchant_data set to "lang=el&basketId=11252". The customer pays, their bitcoin client sends a Payment message, and the merchant's website responds with PaymentACK.message "σας ευχαριστούμε".
Certificates
The default PKI system is X.509 certificates (the same system used to authenticate web servers). The format of pki_data when pki_type is "x509+sha256" or "x509+sha1" is a protocol-buffer-encoded certificate chain:
message X509Certificates {
repeated bytes certificate = 1;
}
If pki_type is "x509+sha256", then the Payment message is hashed using the SHA256 algorithm to produce the message digest that is signed. If pki_type is "x509+sha1", then the SHA1 algorithm is used.
Each certificate is a DER [ITU.X690.1994] PKIX certificate value. The certificate containing the public key of the entity that digitally signed the PaymentRequest MUST be the first certificate. This MAY be followed by additional certificates, with each subsequent certificate being the one used to certify the previous one. The recipient MUST verify the certificate chain according to [RFC5280] and reject the PaymentRequest if any validation failure occurs.
Extensibility
The protocol buffers serialization format is designed to be extensible. In particular, new, optional fields can be added to a message and will be ignored (but saved/re-transmitted) by old implementations.
PaymentDetails messages may be extended with new optional fields and still be considered "version 1." Old implementations will be able to validate signatures against PaymentRequests containing the new fields, but (obviously) will not be able to display whatever information is contained in the new, optional fields to the user.
If it becomes necessary at some point in the future for merchants to produce PaymentRequest messages that are accepted *only* by new implementations, they can do so by defining a new PaymentDetails message with version=2. Old implementations should let the user know that they need to upgrade their software when they get an up-version PaymentDetails message.
Implementations that need to extend messages in this specification shall use tags starting at 1000, and shall update the wiki page at https://en.bitcoin.it/wiki/Payment_Request to avoid conflicts with other extensions.
References
BIP 71 : Payment Protocol bitcoin: URI extensions
BIP 72 : Payment Protocol mime types
Public-Key Infrastructure (X.509) working group : http://datatracker.ietf.org/wg/pkix/charter/
Protocol Buffers : https://developers.google.com/protocol-buffers/
See Also
Javascript Object Signing and Encryption working group : http://datatracker.ietf.org/wg/jose/
Wikipedia's page on Invoices: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Invoice especially the list of Electronic Invoice standards
sipa's payment protocol proposal: https://gist.github.com/1237788
ThomasV's "Signed Aliases" proposal : http://ecdsa.org/bitcoin_URIs.html
Homomorphic Payment Addresses and the Pay-to-Contract Protocol : http://arxiv.org/abs/1212.3257